This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Concepts
- 1: Transgene Expression
- 2: Split Expression
- 3: Templates
- 4:
- 5: Bridging Registrations
1 - Transgene Expression
Here we present details of how single transgenes are curated
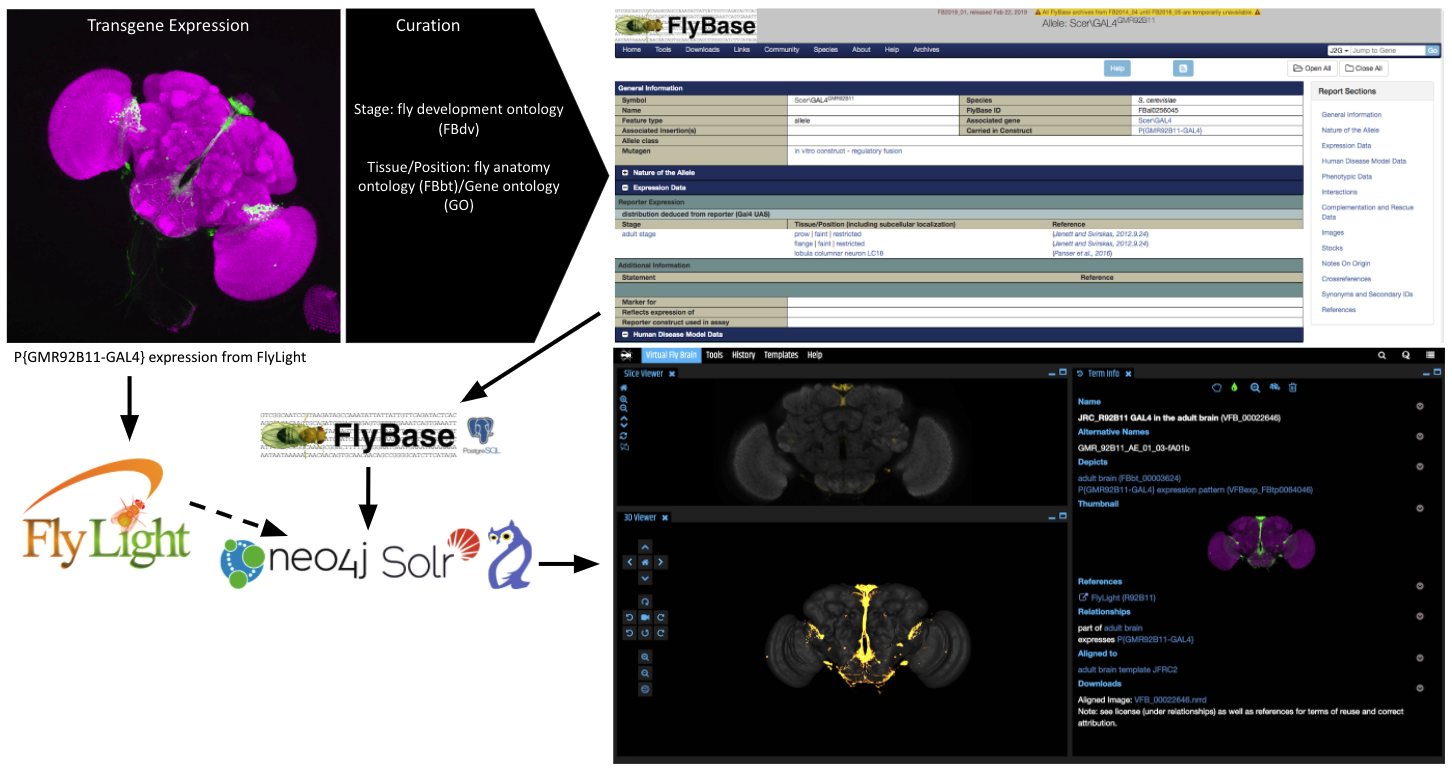
Expression of single transgenes are curated from the published literature into FlyBase as expression statements. Virtual Fly Brain (VFB) combines hosted images with neuroanatomical, expression and genetic data from FlyBase in Neo4j and maps them onto Central Nervious System (CNS) templates where they can be queried using Web Ontology Language (OWL) and Solr.
2 - Split Expression
Thousands of hemi-driver transgenes are now available, meaning that millions of combinations/splits are possible, each targeting some precise subset of the 10s-100s of thousands of neurons in a fly Central Nervous System (CNS). Finding the right combination for an experiment is a serious bottleneck for researchers.
FlyBase & Virtual Fly Brain (VFB) solve this problem by curating information and images recording where expression is driven by combinations of hemi-drivers. Each combination gets a standard name on VFB reflecting the names of the component hemidrivers (see figure below) and is also associated with any short names for the combination used in the literature (e.g. “P{VT017411-GAL4.DBD} ∩ P{VT019018-p65.AD} expression pattern” has_exact_synonym: SS02256")
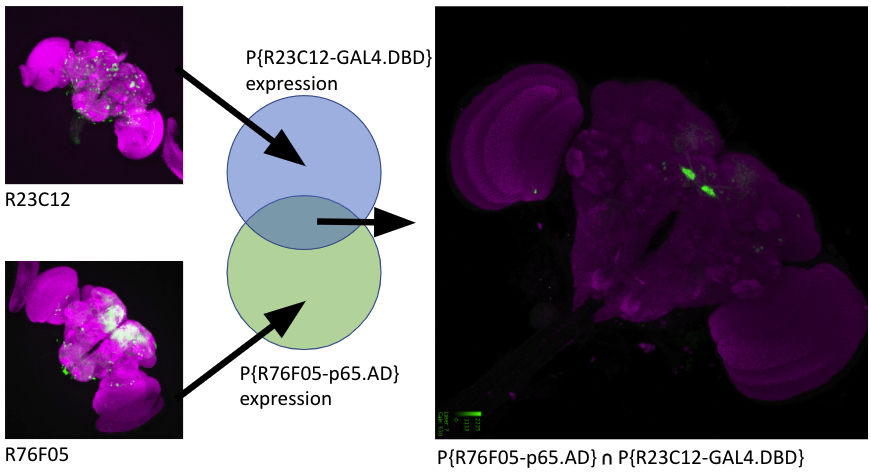

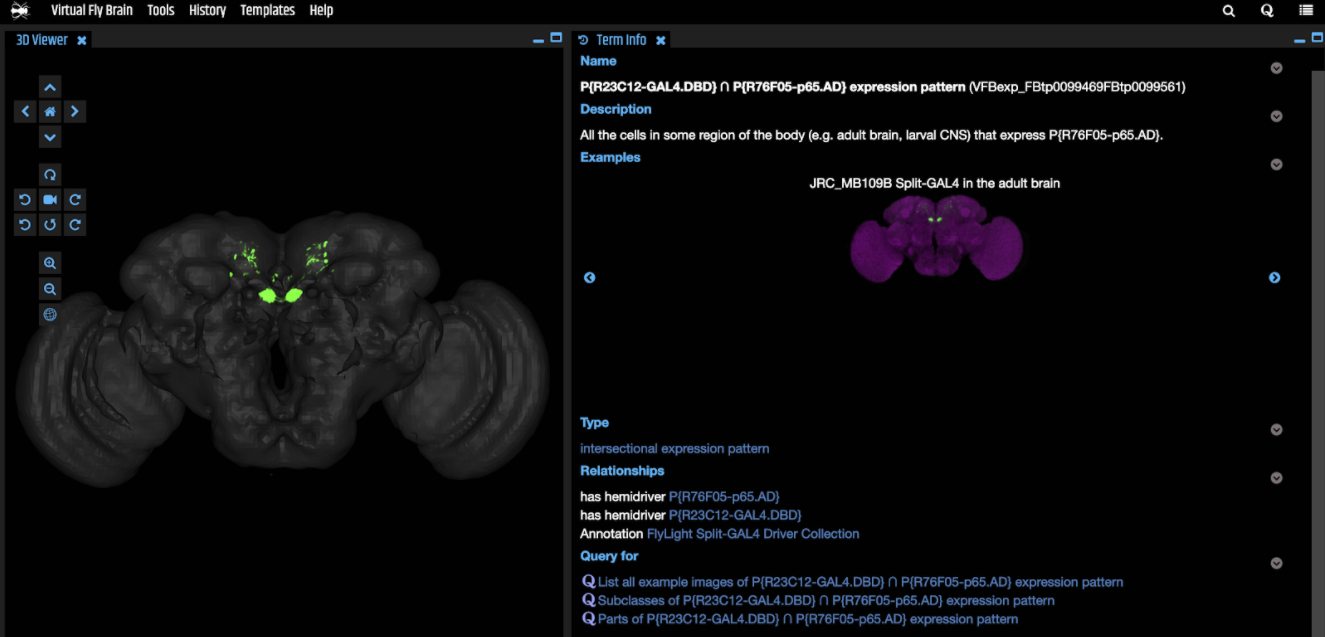
We use programmatic methods to generate expression statements for hemi-driver combinations with FlyLight image data hosted by VFB. Combinations are validated against a local copy of the FlyLight dataset and a structured user readable comment is generated as part of the expression statement. These hyperlink to the partner hemi-driver in FlyBase, contain the strain designation (where available) and can be automatically parsed by Virtual Fly Brain to attach expression and genetic data to a node representing the intersection.
3 - Templates
Many central nervious system (CNS) templates exist for Drosophila, below we provide a summary of those used in VFB.
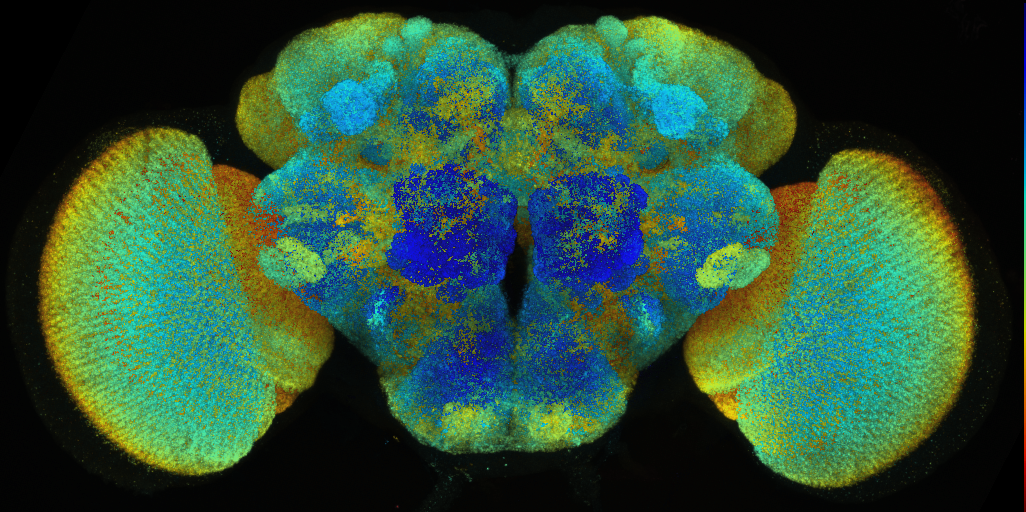
Central Nervious System from Janelia Research Campus JRC2018
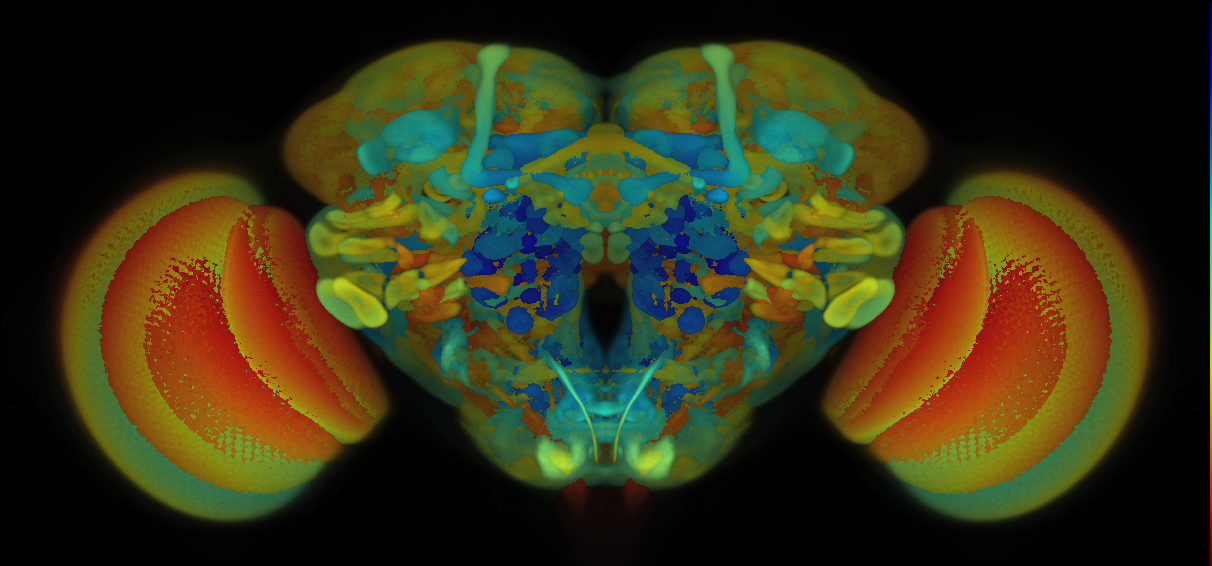
VFB displays data aligned to either the JRC 2018 unisex brain template for cephalic or JRC 2018 unisex Ventral Nerve Cord (VNC) for non-cephalic data.
Bogovic et al., “An unbiased template of the Drosophila brain and ventral nerve cord”
We recomend downloading templates from the VFB browser or the links below however the original files are available from Janelia: JRC 2018 Brain templates
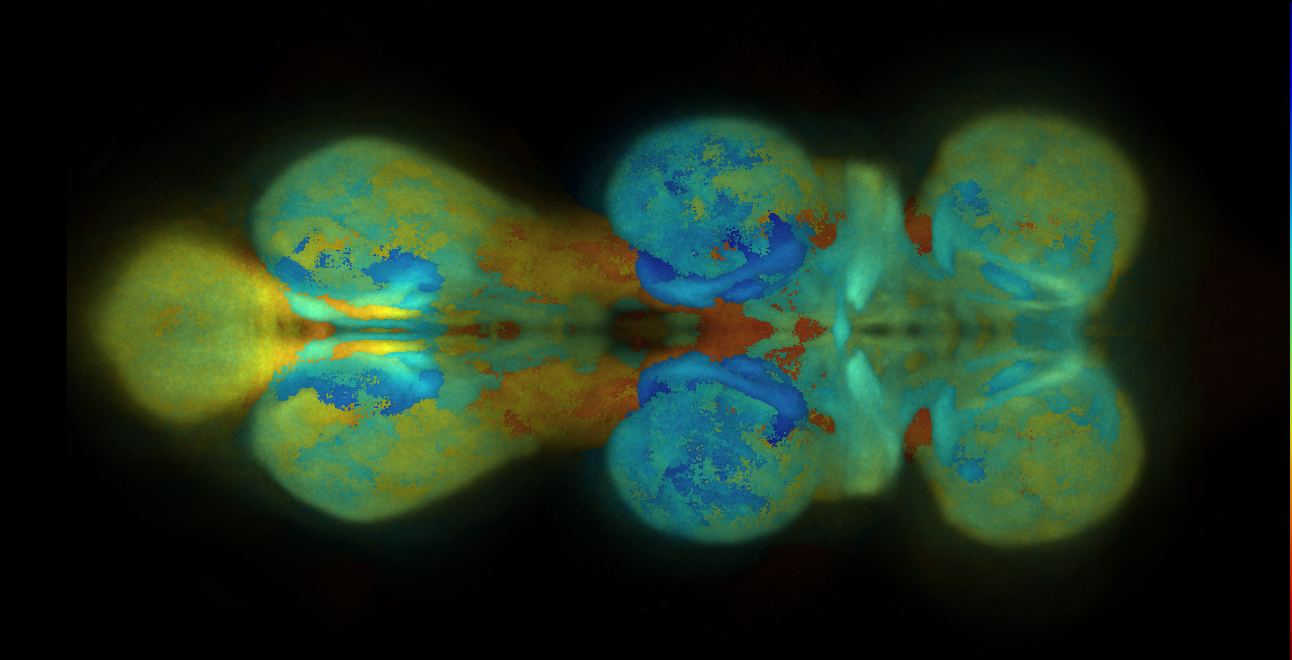
Adult Brain from Janelia Research Campus/VFB (JFRC2010/JFRC2)
Superceeded by JRC2018
Template brain created by Arnim Jenett (Janelia Research Campus), Kazunori Shinomiya and Kei Ito (Tokyo University) from a staining with the neuropil marker nc82.
The voxel size is 0.62x0.62x0.62 micron.
The files are available here.
Painted domains/regions in the available templates
4 -
5 - Bridging Registrations
Many transforms to map between different Drosophila template brains are available.
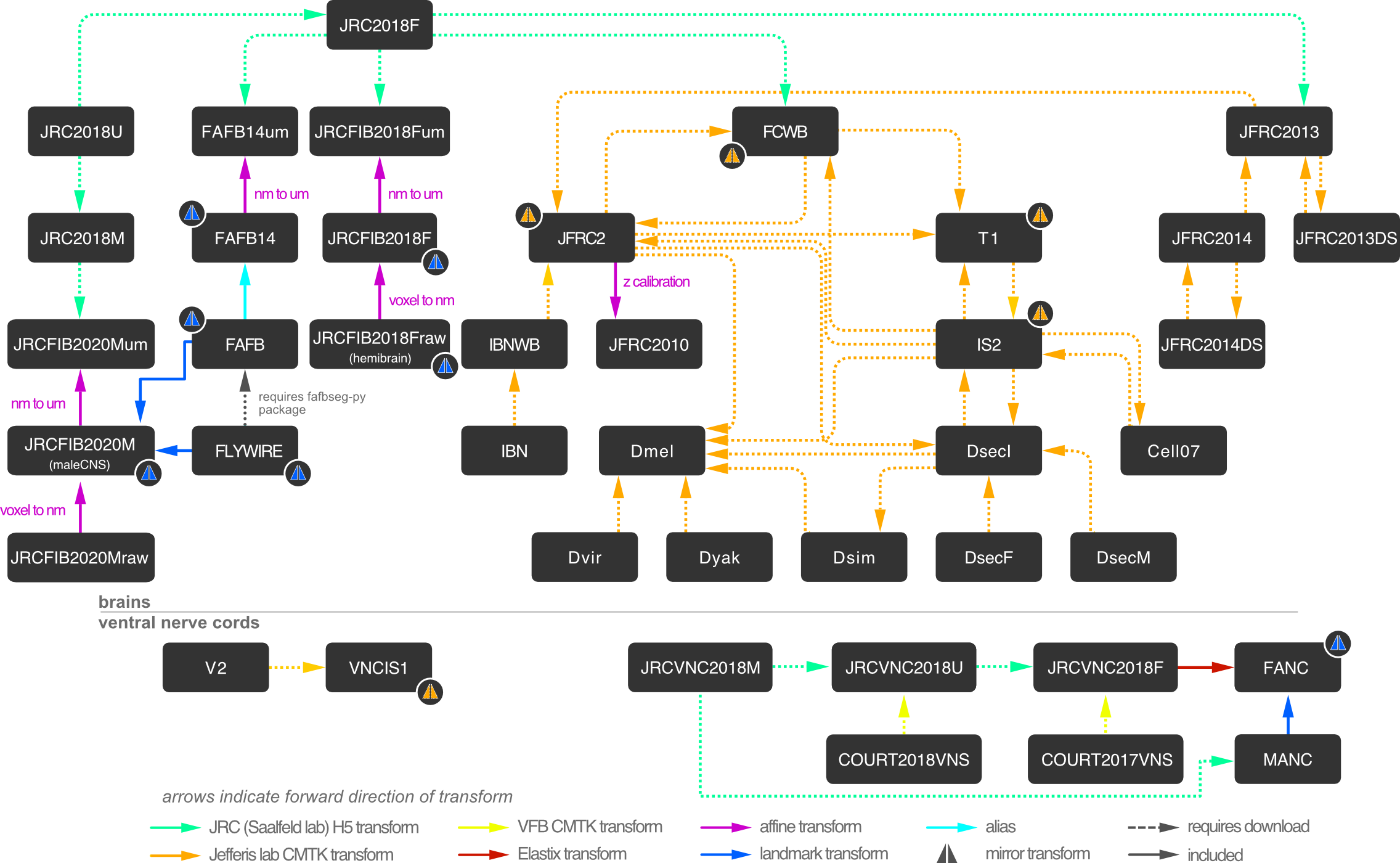
You can see how to use the above in python using navis-flybrains or in R using nat.flybrains